Éxito de los tenistas Veteranos de Montemar
Campeonato de la Comunidad Valenciana de Veteranos/as individual y dobles Los tenistas veteranos de Montemar no dejan de darnos...
Gran temporada de nuestra sección de fútbol
3 equipos campeones de su categoría El 18 de Junio tuvo lugar el acto de entrega de trofeos por parte de la FFCV en el Palau...
VI Torneo de tenis ITF Veteranos en Montemar MT400
Del 25 al 29 de Agosto Montemar retoma su incursión en los torneos internacionales de tenis para veteranos (a partir de 30...
Clase Gratuita de Bachata y Salsa
Tendrá lugar el martes 8 de Julio en Montemar Albufereta Es un placer para nosotros invitarte a una clase gratuita de Bachata y...
Campus y Escuelas de Verano Montemar 2025
El verano está cada vez más cerca, y dentro de muy poco estaremos disfrutando de las esperadas actividades, Campus y escuelas de...
Disfruta del Verano al Ritmo de Zumba
Andrés, nuestro profesor de Zumba, sigue a pleno rendimiento y con ganas de enseñaros los ritmos zumberos más actuales. Pocas...
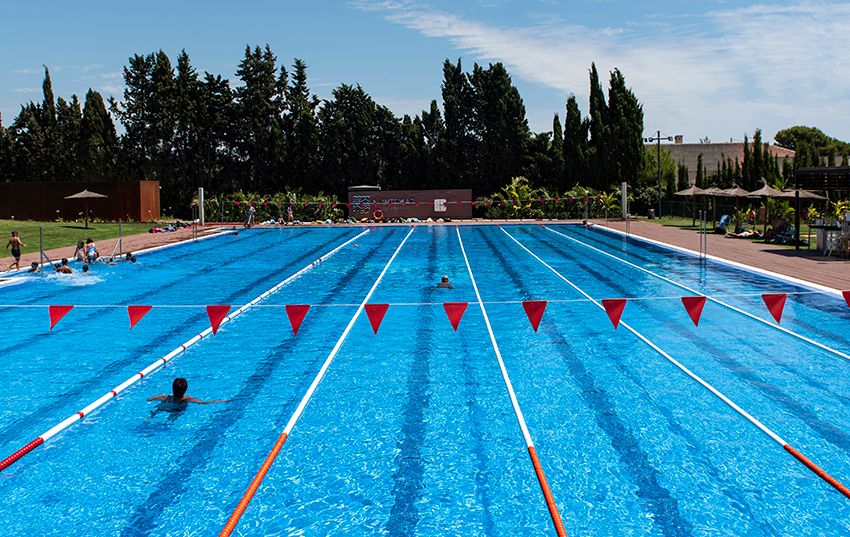
CURSOS DE NATACIÓN TODO EL AÑO
Aprende la técnica de los actuales campeones olímpicos en nuestra piscina de 50 metros, la única de la Comunidad Valenciana climatizada y al aire libre.
LEER MÁS
TIENDA OFICIAL DEL CLUB
Deportes Match, la tienda oficial del Club Atlético Montemar, quiere agradecer un año más el compromiso y fidelidad de sus socios y clientes.
LEER MÁS
HAZ TU RESERVA
COMPETICIONES
Nuestras Escuelas